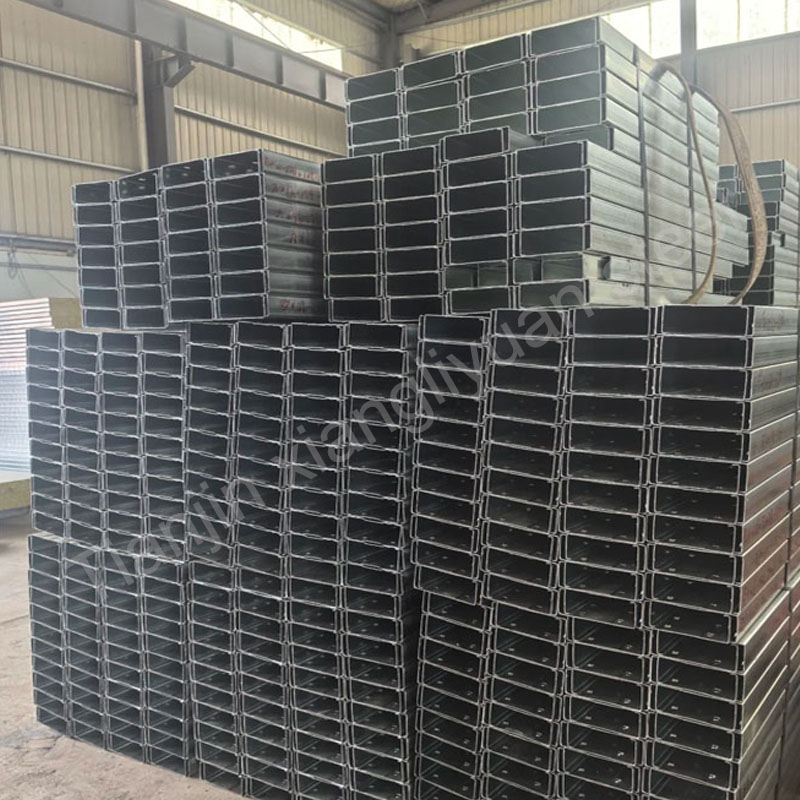
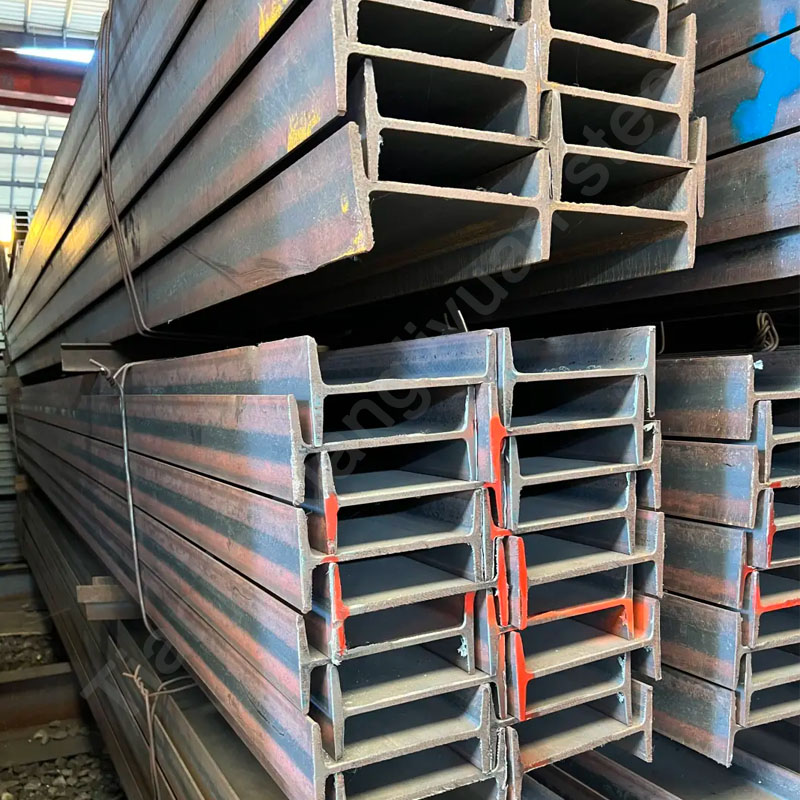
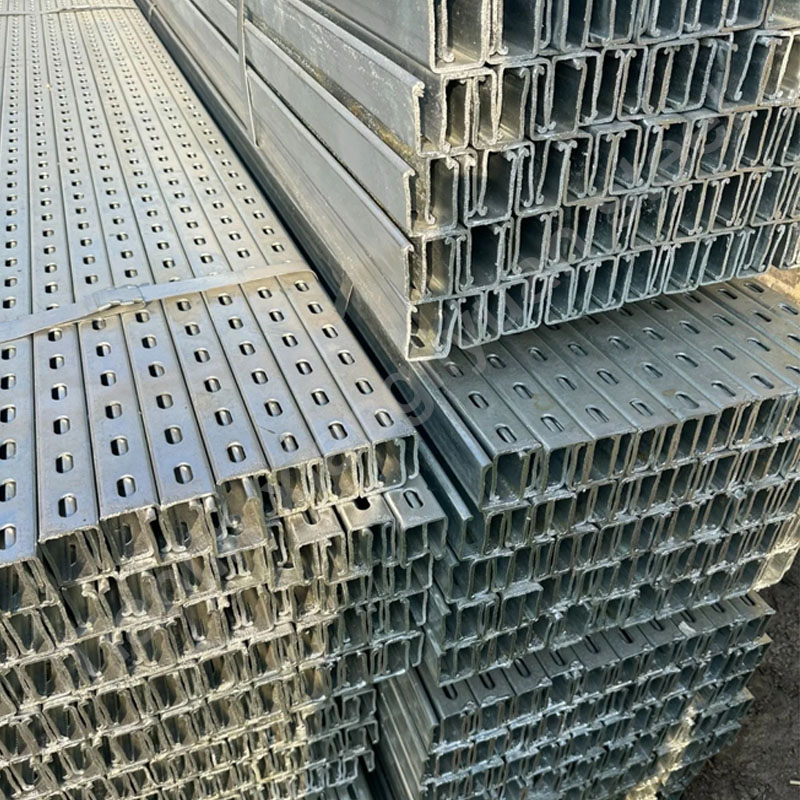
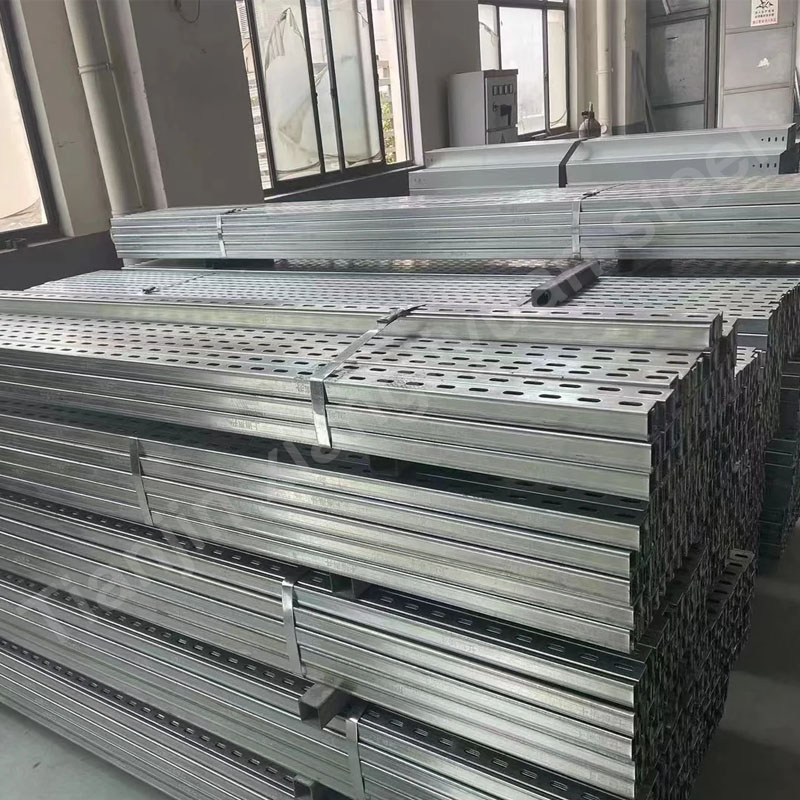
Galvanized C-shaped beams are made of carbon steel or low-alloy high-strength steel, and the surface is hot-dip galvanized to form a zinc coating to prevent steel oxidation and corrosion. Commonly used materials include Q195, Q235, Q345, etc. The specific material selection depends on the use environment and load requirements.
Regarding standards, the production and quality control of galvanized C-shaped beams follow the following main standards:
GB/T 3091-2015: Standard for welded steel pipes for low-pressure fluid transportation, applicable to welded steel pipes.
GB/T 6725-2008: Standard for cold-formed thin-walled steel sections, applicable to the cross-sectional dimensions, technical requirements and inspection methods of C-shaped beams.
ASTM A653/A653M: American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) standard, which specifies the requirements for hot-dip galvanized steel sheets, including zinc layer thickness and adhesion.
JIS G 3302: Japanese Industrial Standard, which specifies the requirements for hot-dip galvanized steel sheets.
After purchasing galvanized C-beams, customers usually need to perform some treatment and processing to better play their role in practical applications. Common processing includes:
Shearing and cutting: According to design requirements, the C-beam is cut into the required length and shape.
Drilling: Drill holes in the beam for easy connection and installation. The location and size of the drilling holes need to be carried out according to the specific design drawings.
Welding and assembly: In some applications, the C-beam needs to be welded or assembled with other components.
Surface treatment: Although the C-beam has been galvanized, in some environments, additional anti-corrosion treatment may be required, such as spraying anti-rust paint.
Galvanized C-beams have a wide range of uses, and common applications include:
Building structure: used for load-bearing structures such as roofs, walls, and floors of buildings.
Solar support: As the main component of the solar panel support, it provides strong support.
Electromechanical installation: used for the installation of electromechanical equipment such as cable trays and pipe supports.
Vehicle manufacturing: used to manufacture the frame and support structure of vehicles such as trucks and trailers.
Agricultural facilities: used to build agricultural facilities such as greenhouses and livestock sheds.
Galvanized C-shaped beams have the following characteristics and advantages:
Excellent anti-corrosion performance: The galvanized layer effectively prevents oxidation and corrosion of steel, greatly extending the service life.
High strength: High-strength steel is used, with good bearing capacity and bending strength.
Light weight: Compared with traditional steel beams, galvanized C-shaped beams are lighter and easier to transport and install.
Convenient construction: Standardized cross-sectional dimensions and processing methods make on-site construction more convenient and faster.
High cost-effectiveness: Compared with materials such as stainless steel, galvanized C-shaped beams have lower costs and lower later maintenance costs.
Good aesthetics: The galvanized layer has a smooth surface and beautiful appearance, which can meet certain decorative requirements.
Good environmental protection: The galvanized layer can be recycled, reducing resource waste and environmental pollution.
In summary, as an important building and industrial material, galvanized C-shaped beams are widely used in many fields due to their excellent anti-corrosion performance, high strength, light weight, and convenient construction. When customers select and use galvanized C-beams, they should choose appropriate materials and specifications based on specific engineering requirements and usage environment, and perform necessary processing and treatment to give full play to their advantages.