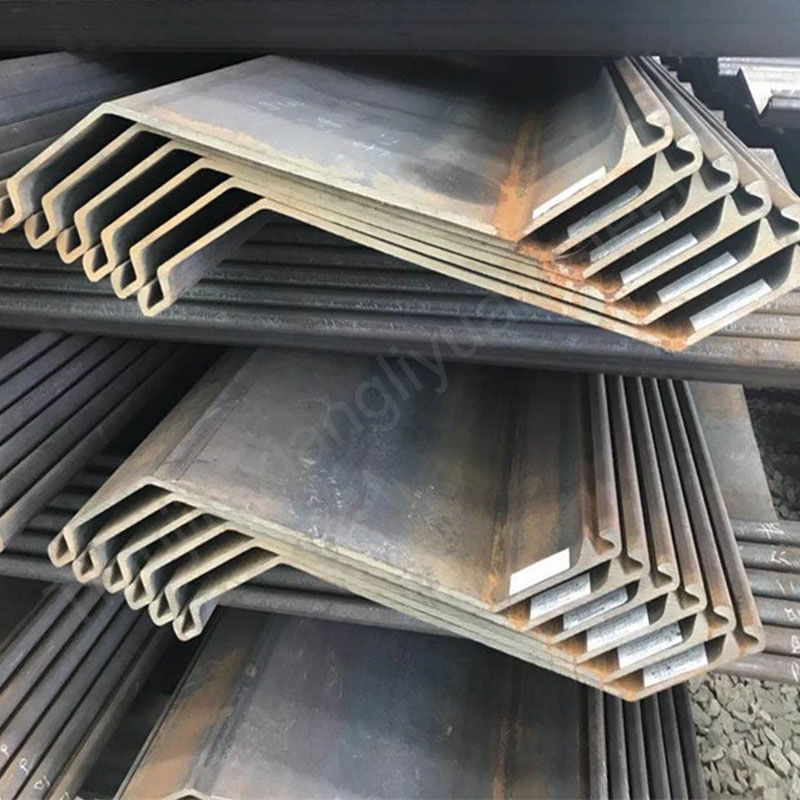
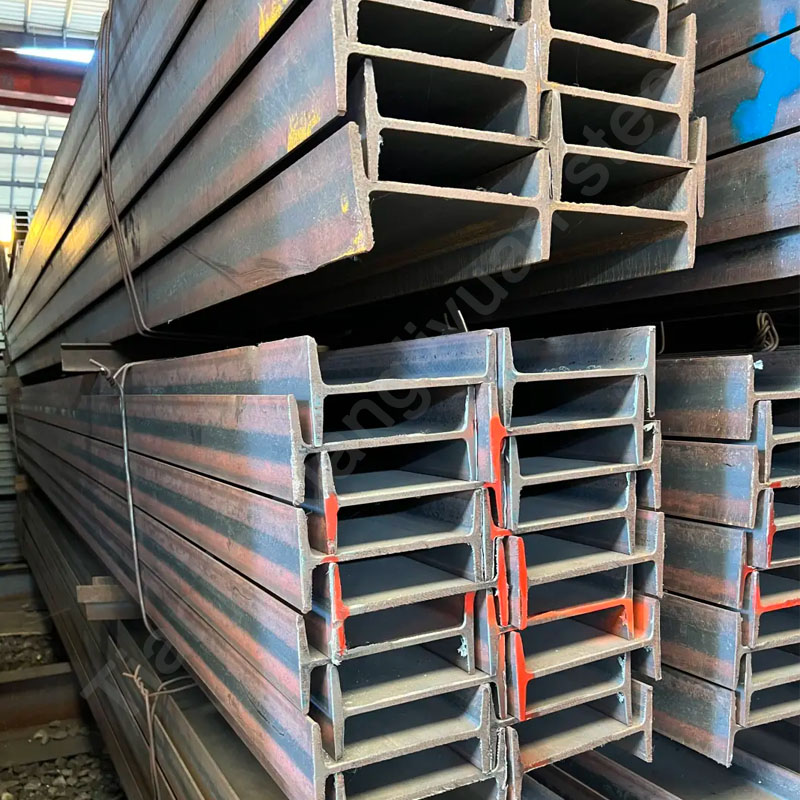
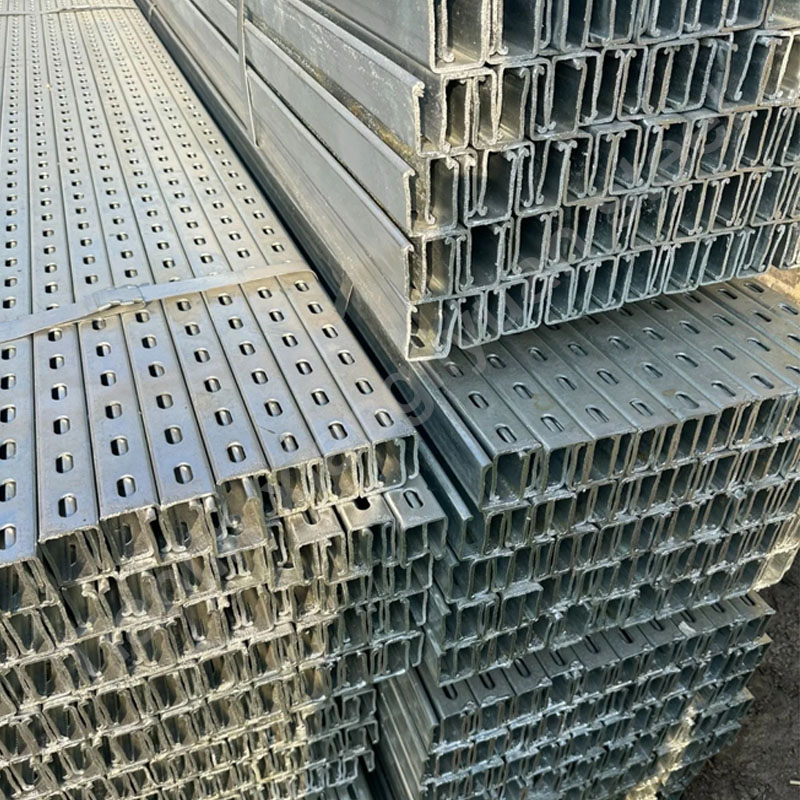
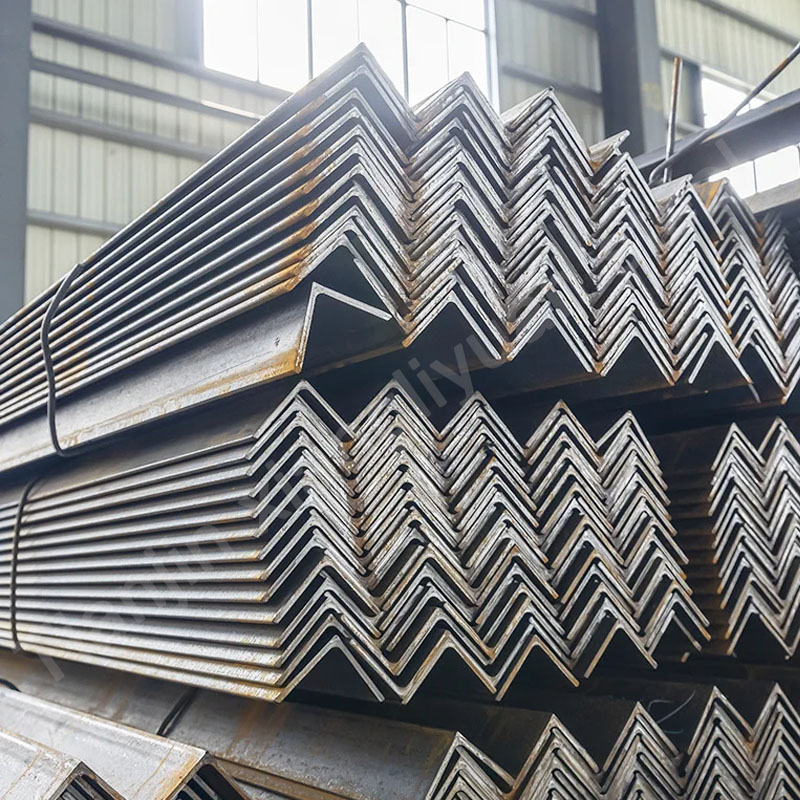
Z-shaped steel is a common cold-formed steel with a cross-sectional shape similar to the letter “Z”. Due to its unique cross-sectional design, Z-shaped steel has good strength and rigidity and is widely used in the construction and industrial fields, especially in steel structure buildings for beams, purlins and supporting structures.
The main materials used for Z-shaped steel are:
Ordinary carbon structural steel: such as Q195, Q235, Q275, etc.
Low alloy high-strength structural steel: such as Q345, Q355, etc.
High-strength steel: such as Q460, etc.
Galvanized steel: often used in environments with high corrosion resistance requirements.
Stainless steel: such as 201, 304, 316, etc., suitable for occasions with high corrosion resistance requirements.
The main production and processing methods of Z-shaped steel are as follows:
Cold bending: The steel strip or steel plate is continuously bent and formed by a cold bending machine. The Z-shaped steel produced in this way has a smooth surface and high dimensional accuracy.
Hot rolling forming: The steel billet is heated to a certain temperature by a hot rolling mill and then rolled into shape. The Z-shaped steel produced in this way has higher strength, but the surface quality and dimensional accuracy are relatively low.
Stamping forming: The steel plate is stamped into shape using molds and stamping equipment, which is suitable for mass production.
The steel grades and standards of Z-shaped steel vary according to different countries and regions. Common standards include:
Chinese standard:
GB/T 13793 “Cold-formed steel”
GB/T 700 “Carbon structural steel”
GB/T 1591 “Low alloy high-strength structural steel”
GB/T 2518 “Continuously hot-dip galvanized steel sheet and strip”
American standard:
ASTM A653 “Standard specification for hot-dip galvanized or aluminum-zinc coated steel sheet and strip”
European standard:
EN 10162 “Cold-formed steel bars”
EN 10025 “Hot-rolled products”
Z-shaped steel is widely used in construction and industrial fields. Its main uses include:
Building structure: such as purlins, beams, longitudinal beams, etc. of steel structure workshops, warehouses, carports, hangars, etc.
Bridge engineering: used for secondary beams and beams of bridges.
Machinery manufacturing: such as structural parts of agricultural machinery and industrial equipment.
Automotive industry: used for carriages, cargo compartments and other parts.
Solar bracket: a supporting structure for photovoltaic power generation equipment.
Advantages
High strength: The cross-sectional design of Z-shaped steel gives it high strength and rigidity.
Lightweight: Compared with traditional steel, Z-shaped steel has the advantage of light weight, which reduces the weight of the building.
Convenient construction: Standardized production and processing methods make Z-shaped steel quick to install, reducing construction time and cost.
Good anti-corrosion performance: galvanized Z-shaped steel has good corrosion resistance and extends its service life.
In general, Z-shaped steel is a structural material with excellent performance and wide application, playing an important role in modern construction and industry.