Introduction to Steel Sheet Piles
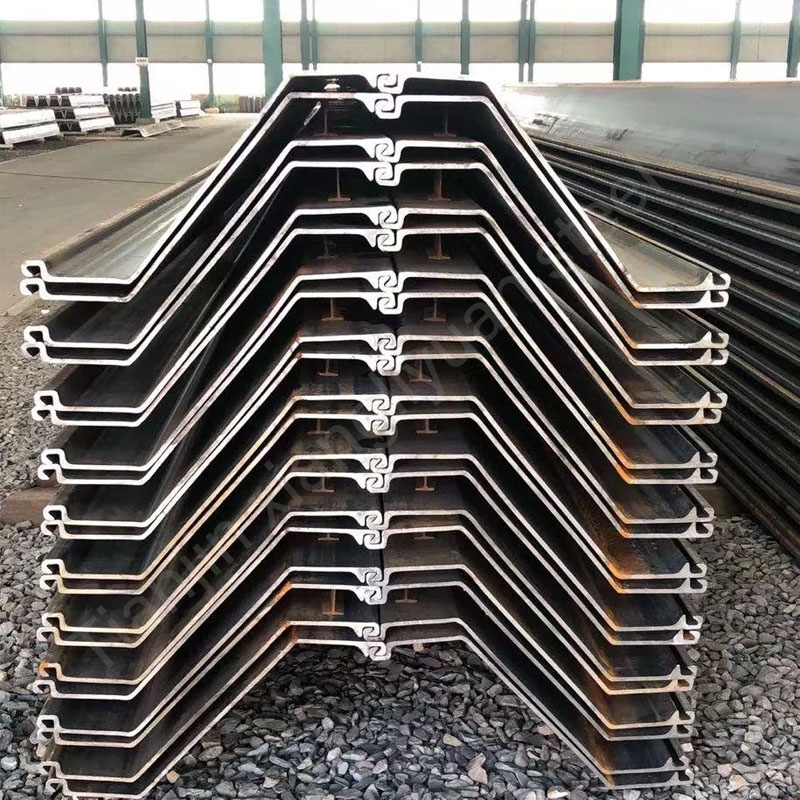
Steel sheet piles, also known as sheet piling or steel piling, are interlocking steel sections driven into the ground to create retaining walls, cofferdams, flood barriers, and foundation supports. Their unique design—featuring a series of grooves and tongues—allows them to form continuous, watertight barriers capable of resisting soil pressure, water flow, and structural loads. Widely used in civil engineering, marine construction, and infrastructure projects, steel sheet piles are valued for their high strength, durability, and ease of installation.
This article explores the material grades, classifications, international standards, dimensional specifications, and applications of steel sheet piles. Whether you’re a contractor, engineer, or project manager, this guide will help you select the right sheet piling solution for your project’s requirements.
Key Materials and Steel Grades
Steel sheet piles are manufactured from hot-rolled or cold-formed steel with tailored chemical compositions to meet strength, corrosion resistance, and weldability needs. Common grades include:
1. Carbon Steel Sheet Piles
ASTM A572 Gr. 50 (USA): High-strength low-alloy (HSLA) steel for general-purpose applications.
EN 10248 S355GP (Europe): Non-alloy structural steel with 355 MPa yield strength.
JIS A 5528 SY295 (Japan): Rolled steel for port and harbor structures.
GB/T 20933 Q345B (China): Low-alloy steel for civil engineering and marine projects.
2. Corrosion-Resistant Sheet Piles
ASTM A690 (USA): Weathering steel for marine environments (e.g., docks, seawalls).
EN 10249 S355J0WP (Europe): Atmospheric corrosion-resistant steel (Corten-like).
Galvanized Sheet Piles: Zinc-coated for enhanced rust protection in coastal zones.
3. High-Strength Sheet Piles
ASTM A572 Gr. 65 (USA): Ultra-high tensile strength for deep excavations.
EN 10248 S430GP (Europe): Heavy-duty steel for demanding infrastructure.
Classification of Steel Sheet Piles
Sheet piles are categorized based on profile design, interlocking mechanism, and application-specific performance:
1. By Profile Shape
U-Type Sheet Piles:
Classic U-shaped cross-section for moderate loads.
Common in temporary cofferdams and riverbank stabilization.
Z-Type Sheet Piles:
Zigzag profile for higher bending resistance and interlock strength.
Ideal for permanent marine structures (e.g., quay walls).
Straight Web Sheet Piles:
Flat, lightweight sections for simple retaining walls and trench shoring.
2. By Interlock Type
Larssen Interlock: Standard interlock for U- and Z-type piles, providing watertightness.
Ball-and-Socket Interlock: Enhanced interlocking for complex geometries and heavy loads.
3. By Application
Temporary Sheet Piles: Reusable sections for short-term projects (e.g., excavation support).
Permanent Sheet Piles: Coated or alloyed for long-term durability in marine or corrosive environments.
International Standards for Steel Sheet Piles
Global standards ensure compliance with mechanical properties, tolerances, and testing protocols:
| Standard | Region | Key Specifications |
|---|---|---|
| ASTM A572/A690 | USA | High-strength and marine-grade sheet piles. |
| EN 10248/10249 | Europe | Hot-rolled and corrosion-resistant sheet piles. |
| JIS A 5528 | Japan | Steel sheet piles for port and harbor works. |
| GB/T 20933 | China | Technical requirements for steel sheet piles. |
| AS/NZS 3679.1 | Australia | Structural steel sheet piles for engineering. |
Standard Dimensions and Specifications
Steel sheet piles are available in standardized sizes to suit diverse project scales:
U-Type Sheet Pile Sizes (EN 10248)
| Designation | Width (mm) | Depth (mm) | Thickness (mm) | Weight (kg/m²) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PU 8 | 400 | 100 | 8.0 | 76.1 |
| PU 12 | 500 | 125 | 12.0 | 112.5 |
| PU 18 | 600 | 170 | 18.0 | 204.0 |
Z-Type Sheet Pile Sizes (ASTM A572)
| Designation | Width (mm) | Depth (mm) | Thickness (mm) | Weight (kg/m²) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AZ 13 | 600 | 200 | 13.0 | 121.8 |
| AZ 18 | 700 | 250 | 18.0 | 180.5 |
| AZ 26 | 800 | 300 | 26.0 | 254.3 |
Common Lengths: 6m to 24m (customizable for project depth).
Applications of Steel Sheet Piles
Steel sheet piles are indispensable in the following sectors:
Marine and Coastal Engineering:
Seawalls, quay walls, and breakwaters.
Dock construction and shipyard basins.
Civil Engineering:
Retaining walls for highways, bridges, and tunnels.
Foundation pits and basement excavations.
Flood Prevention:
Levees, floodgates, and riverbank reinforcement.
Infrastructure:
Underground parking lots, subway stations.
Pipeline trench shoring.
Environmental Projects:
Contaminated soil containment barriers.
Landfill cut-off walls.
Why Choose Steel Sheet Piles?
Rapid Installation: Driven or vibrated into place with minimal site disruption.
Reusability: Temporary piles can be extracted and reused, reducing costs.
Environmental Resistance: Coatings (e.g., epoxy, galvanized) extend service life in harsh conditions.
Design Flexibility: Compatible with anchors, walers, and tie-backs for complex geometries.
How to Select the Right Steel Sheet Piles
Soil and Load Conditions:
Soft soils require deeper sections (e.g., Z-type) for stability.
High groundwater levels demand watertight interlocks (Larssen type).
Corrosion Risks:
Choose ASTM A690 or galvanized piles for saltwater exposure.
Project Duration:
Temporary projects benefit from reusable carbon steel piles.
Permanent structures need coated or alloyed steel for longevity.
Steel sheet piles are a cornerstone of modern construction, offering unmatched versatility for retaining walls, marine structures, and flood defenses. By selecting the appropriate profile (U-type, Z-type), material grade (ASTM A572, EN S355GP), and corrosion protection, engineers can ensure project success across diverse environments.
For companies seeking reliable sheet piles, working with a certified manufacturer ensures compliance with ASTM, EN and JIS standards. Explore Tianjin Xiangliyuan Steel’s range of hot-rolled, galvanized and high-strength sheet piles tailored for civil engineering, marine engineering and infrastructure projects.